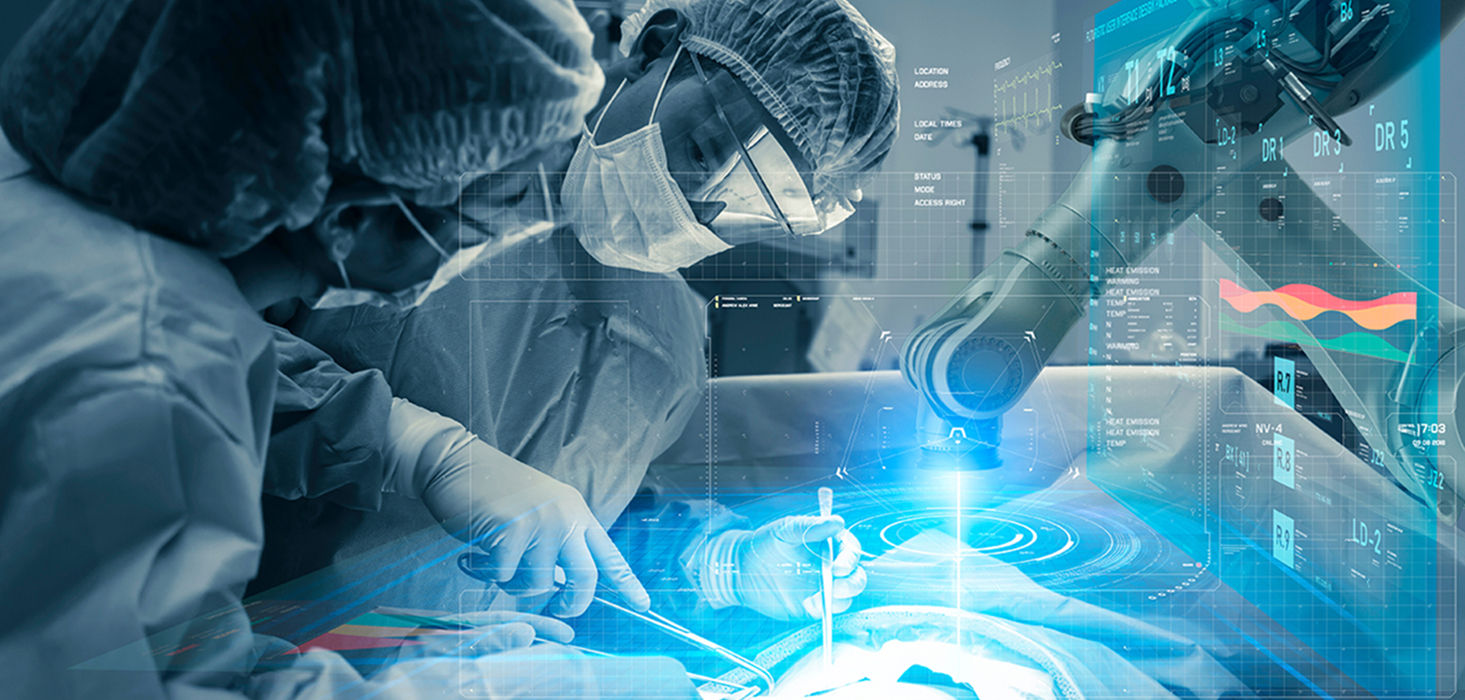
The medical industry has always been characterized by continuous innovation and progress, with a constant stream of new technologies and techniques being developed and improved to enhance patient outcomes and healthcare in general. In recent years, one of the most notable breakthroughs has been the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) tools into various aspects of medical practice, including diagnostics, treatment planning, and surgical procedures. The field of robotic surgery, in particular, has experienced significant expansion and advancement, with AI-based systems now being utilized to aid surgeons in executing intricate and delicate procedures with unprecedented precision and accuracy.
The medical technique of robot-assisted surgery, also referred to as robotic surgery, entails the utilization of computer-controlled robotic systems to execute surgical procedures, either entirely or partially. These systems usually comprise a surgeon’s console, where the surgeon manages the robotic arms, and a patient-side cart, where the robotic arms and surgical instruments are located. The surgeon observes the surgical site through a high-definition, 3D camera and operates the robotic arms using hand and foot controls, enabling accurate and regulated movements during the procedure.
The da Vinci Surgical System is one of the most renowned robotic surgery systems, having been employed in over six million surgeries across the globe since its inception in 2000. This system has demonstrated exceptional efficacy in urology, gynecology, and general surgery, as evidenced by studies indicating that it can result in decreased blood loss, shorter hospitalization periods, and quicker recuperation times for patients.
The incorporation of AI tools into robotic surgery systems holds immense promise for further transforming the field, with numerous captivating advancements already in progress. A noteworthy instance is the development of the Berkeley Autonomous Robot for the Operating Room (BARO) by scholars at the University of California, Berkeley. This new robotic system is powered by AI and employs machine learning algorithms to scrutinize surgical data and assimilate the movements and methods of skilled surgeons, enabling it to execute surgical procedures with remarkable accuracy and precision.
The utilization of AI-based surgical planning tools represents another encouraging advancement, as these tools can assist surgeons in selecting the optimal method for a given procedure by scrutinizing patient-specific data and generating 3D representations of the surgical site. Moreover, these tools can furnish real-time feedback during the surgery, notifying the surgeon of any probable complications or proposing alternative approaches based on the evolving circumstances.
AI tools can enhance surgical precision and accuracy, reduce human error, and improve patient safety by monitoring surgical instrument movements and providing real-time feedback to the surgeon, as demonstrated by researchers at MIT.
Despite the numerous potential advantages of AI-based robotic surgery, there exist certain challenges and apprehensions that necessitate attention. One of the foremost concerns is the exorbitant cost of these systems, which can impede access for several hospitals and healthcare providers. Furthermore, there is a requirement for continuous research and development to guarantee that AI tools are secure, efficacious, and dependable, along with the necessity of regulatory frameworks and guidelines to oversee their utilization in clinical practice.
To conclude, the incorporation of AI tools into robotic surgery systems demonstrates the immense potential for the future of medicine, with the capability to enhance patient outcomes, minimize complications, and transform the manner in which surgical procedures are conducted. As research and development in this domain progress, it is probable that further pioneering and revolutionary AI applications in the operating room will emerge, fostering a new era of precision medicine and upgraded healthcare for all.